Flow rates
While the vertical measurements to water levels are being made, the measurements of quantity being pumped at those levels is also being made.
The most accurate and fundamental method of measuring the rate of flow of a steady continuous stream of water is by collecting it in a container of known size and measuring the time required to collect it.
Since this method is inconvenient and impractical for the average well job other methods are employed.
These involve the use of Venturi meters, pilot tubes, current meters, orifices, flow gauges, weirs and similar devices.
A description of the use of all these instruments is beyond the scope of this chapter.
Three of the most commonly used methods are as follows:
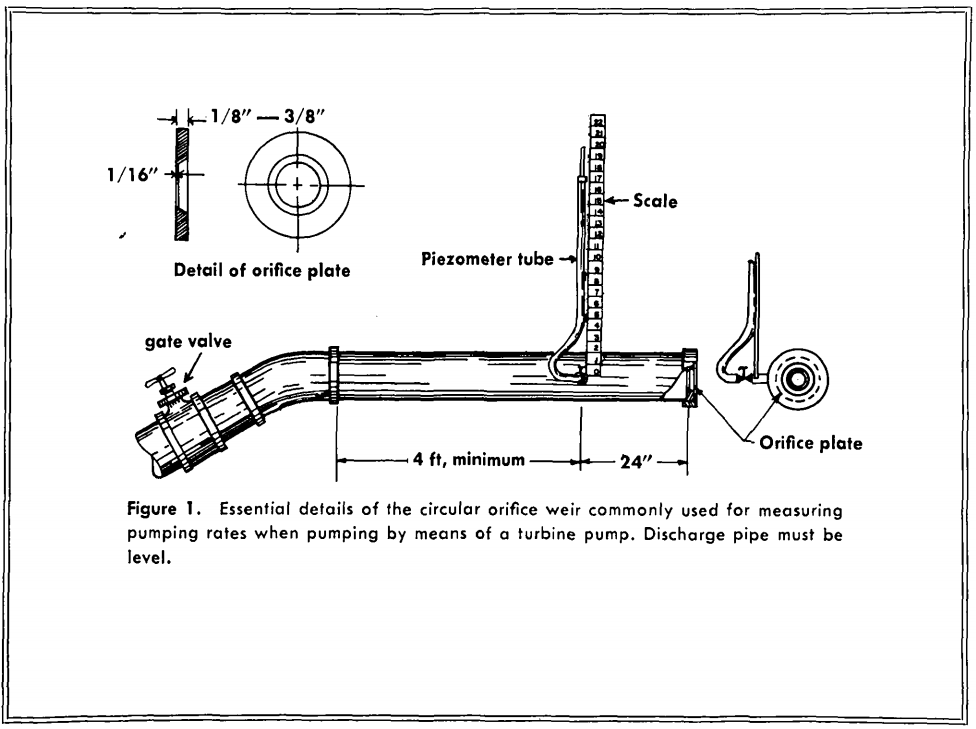
Circular Orifice Weir
The circular orifice weir consists of a steel plate centered over the end of a discharge pipe in which there is a perfectly circular hole with clean edges, smaller in diameter than the discharge pipe.
Back two feet from this plate is a small pipe tapped smoothly at right angles into the discharge pipe at the horizontal center line.
The discharge pipe should be at least six feet long overall.
A clear plastic tube is installed over the small (1/8 inch pipe nipple) pipe and is held vertically during the testing.
The pressure caused by the restriction of the water passing through the orifice plate causes water to rise in the tubing.
The water level in this Piezometer tube is measured from the center of the discharge pipe to the top of the water column.
The amount of water being pumped is a function of this height and is determined from Table No. I.
The accuracy of this method is dependent upon how carefully the well tester observes and understands certain limitations of the instruments.
First, the pipe on which the orifice is used must be horizontal and the discharge must be allowed to fall freely.
Second, the edges of the orifice opening must be sharp and clean, preferably chamfered to 45° with the sharp edge upstream.
Third, combinations of pipe and orifice diameters must be such that the head built up will be at least three times the diameter of the orifice.
Fourth, the orifice must be vertical and centered in the discharge pipe.
Fifth, the head measuring tube must be free from air bubbles and not protrude beyond the inside surface of the pipe.
The apparatus and setup are shown in Figure 1 for all ordinary tests.
Contact: Exmork
Tel: 86-15757781695
Whatsapp: 86-15757781695
Email: exmork@exmork.com
Add: Headquarters Economic Park,Yueqing,Zhejiang,China